 Important: Important: |
|---|
| This is retired content. This content is outdated and is no longer being maintained. It is provided as a courtesy for individuals who are still using these technologies. This content may contain URLs that were valid when originally published, but now link to sites or pages that no longer exist. |
The DirectShow stream architecture is based on filters and pins. Filters communicate with the filter graph manager and with the pins on the filter. Pins connect filters and handle transporting the data down the stream.
CBaseFilteris the base class for all filter classes. It implements the IBaseFilterinterface, which specifies methods that allow the filter graph manager to create and enumerate pins, retrieve filter information, and notify the filter that it has been added to a filter graph. CBaseFilteralso implements the IMediaFilterinterface (from which IBaseFilterderives) to allow the filter to receive run, pause, and stop commands from the filter graph manager. This base class adds member functions to retrieve the pin count, retrieve pointers to individual pins, and retrieve the pin version.
The CBaseMediaFilterclass also implements the IMediaFilterinterface. However, because IMediaFilteris also implemented by CBaseFilter, this class is seldom used except to write a plug-in distributor (PID).
Several classes are derived directly from CBaseFilter. Each of these classes provides a base class for implementing a specific type of filter. These include:
- CSource, a base class for source filters.
- CTransformFilter, a base class for transform filters.
-
CBaseRenderer, a base
class for renderer filters.
The CSourcefilter class works in conjunction with the CSourceStreampin class to help create a source filter. Most of the work is done in the pin class, and CSourceadds pin creation and deletion member functions. The CSourcePositionclass implements a source filter.
The CTransformFilterclass implements a transform filter. Derive your transform class from CTransformFilterif you want to make a copy of the data. The CTransInPlaceFilterclass, derived from CTransformFilter, allows in-place transforms that do not copy the data. These transform filter classes work in conjunction with similarly named pin classes (for example, CTransformOutputPinand CTransformInputPin). Most member functions in the pin classes are implemented to call member functions in the transform filter class, so typically you need only to derive your filter from the filter class and override a few member functions to implement a transform filter.
CTransformFilteradds several member functions to those inherited from CBaseFilter. Some of these are pure virtual member functions that the derived class must override. One example is the CTransformFilter::Transformmember function, which is called when the input pin receives a sample. This member function provides the core of the transform functionality. Other member functions to be overridden also involve implementations that are specific to the derived class, such as verifying media types on pins and allocating the correct amount of memory. Additionally, several CTransformFiltermember functions are called at various points in the connection or streaming process; the derived class can override these to handle requirements such as adding or releasing references to interfaces.
The CVideoTransformFilterclass derives from the CTransformFilterclass and is used as a base class for filters that can affect the quality of a rendered video by dropping frames when the video renderer sends quality-control messages. This class is primarily used by video decompressors in the DirectShow run time.
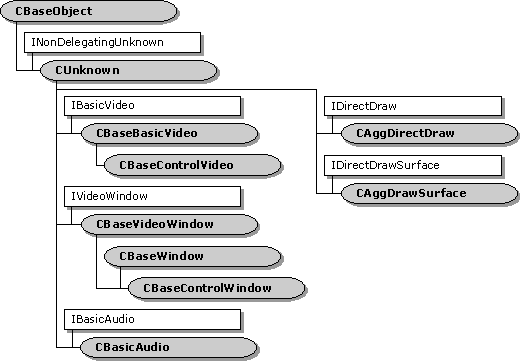
The CBaseRendererclass and its derived class, CBaseVideoRenderer, are the base filter classes that implement a video renderer filter. The video renderer filter used in DirectShow is derived from CBaseVideoRenderer. There are other renderer classes that work in conjunction with these classes but are not derived from CBaseFilter. These classes are:
- CRendererInputPin
- CBaseControlVideoand its base class CBaseBasicVideo
- CBaseControlWindow, and its base classes CBaseVideoWindowand CBaseWindow
- CAggDirectDraw
-
CAggDrawSurface
The following illustration shows all the classes that support renderers that are not derived from either CBaseFilteror CBasePin.
Last updated on Tuesday, May 18, 2004