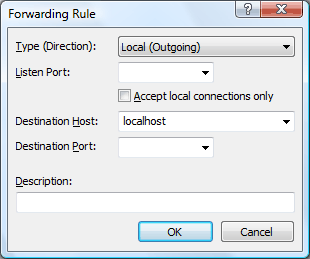
The Forwarding Rule dialog box allows you to add a new TCP/IP port-forwarding rule to a session. To open this dialog box, in the session Properties dialog box, select SSH for the connection method, and then click Add in the SSH: Tunneling page.

Select Local(Outgoing), Remote(Incoming), or Dynamic(SOCKS4/5) depending on the type of the connection.
Most client programs such as pop3, telnet, and ftp are running on your local machine and try to connect to the remote server. So you need to select Local(Outgoing) for those client programs.
For some server programs such as PC X server, and ftp server, the connection comes from the remote server (in which ssh server is running) to your local machine (in which Xshell is running). You need to select Incoming for this kind of connections.
If you are using Xshell as a SOCKS4/5 server, select Dynamic. For an application to use SOCKS4/5 server on Xshell, you must point the PC running Xshell with Dynamic rules setup as its SOCKS server in each application.
Listen PortEnter or select the port to which the client program will try to connect.
For Local(Outgoing) connections, the listen port is allocated by Xshell in your local machine. When a client program in your local machine connects to the listen port, Xshell forwards the connection to the ssh server over a secure tunnel and the ssh server again redirects the connection to the destination port of the destination host.
For Remote(Incoming) connections, the listen port is allocated by the ssh server in the remote host. When a client program in the remote host connects to the listen port, the ssh server forwards the connection to Xshell over a secure tunnel and Xshell again redirects the connection to the destination port of the destination host.
Dynamic(SOCK4/5) forwarding works the same as Local forwarding. It uses the SOCKS protocol and its default port number is 1080.
Accept local connections onlyLocal, and Dynamic forwarding only accept connections from a PC where this session is currently running.
Remote forwarding only accepts connections originated from the server where the session is connected to.
Destination HostEnter the hostname or IP address of the host to which you want to forward connections. If you want to forward a pop3 connection, the destination host will be the host in which the mail server is running. For Incoming connections, it will be "localhost" in most cases.
Destination PortEnter the port number of the destination host to which you want to forward connections. If you want to forward a pop3 connection, the destination port will be the port the mail server is listeninglistening (the default pop3 port is 110).
DescriptionEnter the description for the selected forwarding rule.