
Forwarding Messages to External Applications
HPOM for Windows provides options to forward messages to external applications, including external trouble-ticket or notification software, using the standard interfaces of HPOM.
HPOM for Windows does not provide a dedicated trouble-ticket or notification interface as HPOM for UNIX does. However, a major part of the functionality can be implemented easily by using HPOM for Windows and underlying platform services, particularly the WMI infrastructure on the HPOM for Windows management server. On the server, all HPOM for Windows objects (nodes, services, messages, ...) are represented by WMI objects in HPOM for Windows' own namespace:
You can use regular HPOM for Windows WMI policies to monitor these objects so that any new message that arrives on the management server can trigger an automatic action that forwards the message to an external application in the following sequence:
- The WMI policy catches events triggered by the creation of an instance of the class OV_Message on the HP Operations management server.
- Then the new message can be forwarded to any other party using a script or program bound to the policy rule as an automatic command, as shown in the illustration.
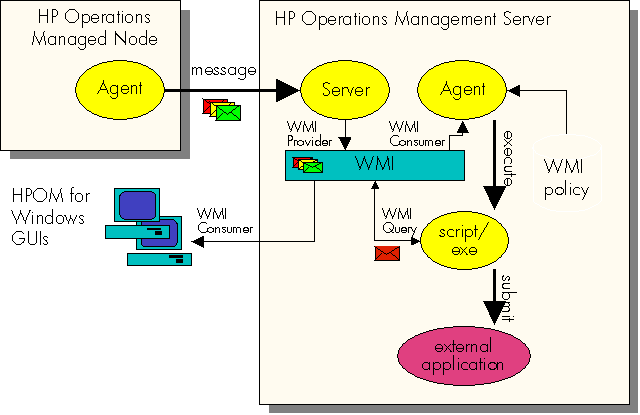
The script itself can perform whatever operations are necessary. In this example, the operation would be to either submit a trouble-ticket or trigger a notification system. The WMI policy can contain as many rules as required, and therefore can match arbitrary messages. The executed export script may be different for each rule.
WMI and HPOM for Windows
WMI, as Microsoft's implementation of WBEM, is used heavily as infrastructure on the HP Operations management server. In addition to the basic CIM objects provided by the operating system, many HPOM for Windows data objects are represented as WMI objects that can be accessed using WMI policies, scripts, or programs. However, these classes are considered internal to HP. They may be modified by HP in subsequent releases and they should be strictly read-only.
HP does not provide any detailed documentation about these classes other than what is available in the HPOM for Windows online help.
The WMI class and instance browsers which are integrated into the HPOM for Windows WMI policy editor can be used to browse through the WMI classes and instances. You can also use the Microsoft tool, wbemtest, to explore WMI classes.
Related topics:
Detailed information:
Examples:
Advanced topics: