 Important: Important: |
|---|
| This is retired content. This content is outdated and is no longer being maintained. It is provided as a courtesy for individuals who are still using these technologies. This content may contain URLs that were valid when originally published, but now link to sites or pages that no longer exist. |
4/8/2010
Windows Mobile devices can be provisioned over-the-air using OMA DM provisioning XML and an OMA Device Management server. This is the preferred method, since it provides two-way communication for subsequent provisioning.
 Note: Note: |
|---|
| Microsoft does not provide an OMA DM server. The OEM, mobile operator, or a third party must create their own server. For information about server requirements, see Server Requirements for OMA Device Management. |
Assumptions
- The device is bootstrapped to communicate with the DM server
and accept management commands from it. For more information, see
Bootstrapping To
Use An OMA DM Server.
 Note:
Note:OTA bootstrapping is disabled by default in Windows Mobile devices. Before you can bootstrap or continuously provision the device OTA you must enable OTA bootstrapping. For more information see Enabling OTA Bootstrapping. - You have created OMA DM provisioning XML as described in
Creating a
Provisioning XML File.
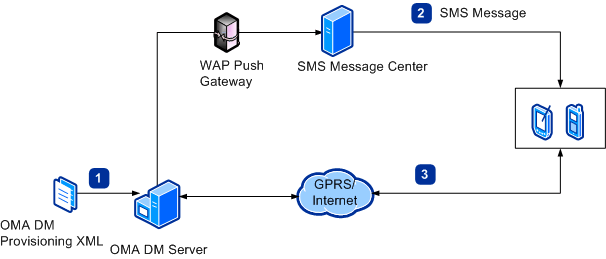
The following illustration shows how a device is provisioned using an OMA DM server.

The numbers in the illustration correspond to the following steps:
- You place the OMA DM provisioning XML file on the OMA DM server
to be ready for download.
- Using a WAP push, the DM server sends a Short Message Service
(SMS) message to the device. The message, also called the server
trigger, includes the server ID and tells the client device to
initiate a session with the server. The client device will use this
information to verify that the server is authorized to communicate
with it.
- The device initiates a DM session with the OMA DM server and
downloads the OMA DM provisioning XML file.
The device is updated.
For greater detail of what occurs on the device, see OMA DM version 1.1.2 Architecture.
For information about what occurs during a DM session, see The Device Management (DM) Session.








 See Also
See Also