 Important: Important: |
|---|
| This is retired content. This content is outdated and is no longer being maintained. It is provided as a courtesy for individuals who are still using these technologies. This content may contain URLs that were valid when originally published, but now link to sites or pages that no longer exist. |
4/8/2010
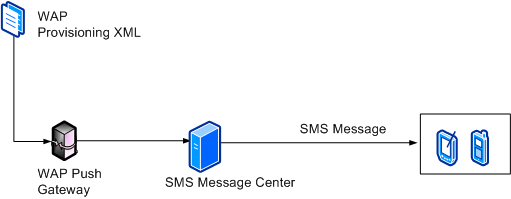
You can push a provisioning XML file over the air (OTA) to a Windows Mobile device using a one-way WAP push and the OMA Client Provisioning protocol. This method is useful if the mobile operator prefers to bootstrap the device over the air at the point of sale or after purchase.
 Note: Note: |
|---|
| Microsoft does not provide an OMA Client Provisioning server. The OEM, mobile operator, or a third party must create their own server. For information about server requirements, see Server Requirements for OMA Client Provisioning. |
Assumptions
- The device is bootstrapped to communicate with the OMA Client
Provisioning server. For more information, see
Bootstrapping To
Use an OMA Client Provisioning Server.
 Note:
Note:OTA bootstrapping is disabled by default in Windows Mobile devices. Before you can bootstrap or continuously provision the device OTA you must enable OTA bootstrapping. For more information see Enabling OTA Bootstrapping. - You have created OMA Client Provisioning XML as described in
Creating a
Provisioning XML File.
The following illustration shows how a device is provisioned using an OMA Client Provisioning server.

The illustration shows the dataflow explained in the following steps:
- A provisioning XML file is placed on the OMA Client
Provisioning server, also known as the WAP Push Gateway.
- Using a WAP push, the server sends a Short Message Service
(SMS) message that contains the WAP provisioning XML file to the
device.
The device is updated.
For greater detail of what occurs on the device, see OMA Client Provisioning Device Management Architecture.








 See Also
See Also