When you run a synchronization package, the rules specified in that package determine what happens to new records and updates to fields in existing records. This lets you protect existing data and control which records are added to the destination asset.
New records can either be inserted directly into the destination asset, or can be sent to the Pending inserts queue for manual review before insertion.
Updates to existing data in specified columns can either be added directly to the destination asset, overwriting the existing value, or can be sent to the Pending updates queue for manual review before acceptance into the destination asset.
NOTE: In most cases, Pending inserts and Pending updates should only be enabled in the context of smaller synchronization jobs where you may not want certain records to be changed from an external data source. Its purpose is to facilitate careful examination of asset records that you anticipate in advance may require a line-by-line verification to decide whether the record should be inserted, ignored, or deleted.
See Task 4: Rules panel settings in Synchronization wizard for information on how to use rules when creating a synchronization package.
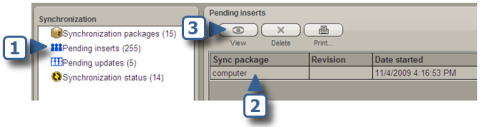
If you don't check the Automatically add new items from the source to the asset system checkbox in a synchronization package, all new records created by running that package are sent to the Pending inserts queue instead of being added directly to the destination asset or resource. Records in the queue are only added to the destination if you choose to insert them. Pending inserts remain in the queue until you choose to insert, ignore, or delete them.

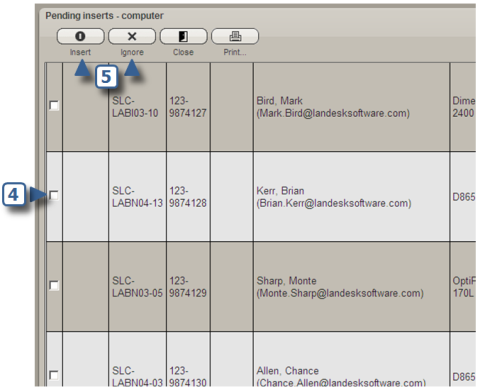
As in this example, a list of the pending inserts appears.
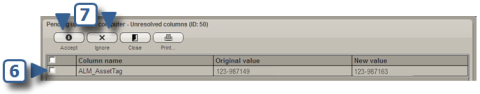
If you check one or more items in the Protected destination columns list in a synchronization package, current data in that column of the destination asset is protected against being overwritten when you run the package. Instead, any updates to values in the protected columns are sent to the Pending updates queue where you can review them. Pending updates will remain in the queue until you choose to either accept or ignore them.
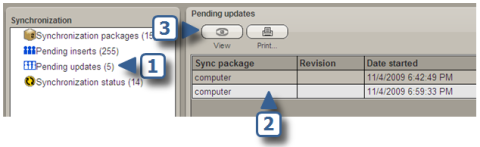
As in this example, you'll see a list of the records for which
there are pending updates.
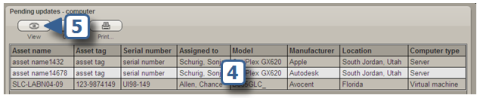
As in this example, you'll see the column name for each item of unresolved data, the original value, and the new value that was returned when the synchronization package was run.